Iran's Population: Unveiling Demographic Shifts & Future Trends
The demographic landscape of any nation tells a profound story of its past, present, and future. For Iran, a country with a rich history and a pivotal role in the Middle East, its population dynamics are particularly fascinating. From rapid growth in the late 20th century to a notable slowdown in recent years, understanding the "population in Iran" requires a deep dive into various factors, including birth rates, urbanization, and age structure. This article aims to provide a comprehensive overview, drawing on the latest statistics and projections to illuminate the intricate patterns shaping Iran's human tapestry.
Exploring the nuances of Iran's population isn't just about numbers; it's about understanding the societal, economic, and environmental implications of these changes. As a nation of over 90 million people, Iran's demographic journey reflects broader global trends while also presenting unique challenges and opportunities specific to its cultural and political context. We will examine key indicators such as growth rates, median age, and urbanization, offering insights into what these trends mean for the country's future.
Current Population Snapshot: A Glimpse into Iran Today
As of November 2024, Iran's population stands at approximately 91.5 million people. This figure is a dynamic one, constantly updated by births, deaths, and migration. Looking slightly ahead, the total population in Iran is projected at 91,567,738, or 91.57 million people, for the year 2024. This number is based on the de facto definition of population, which meticulously counts all residents, regardless of their legal status or citizenship, providing a comprehensive picture of those living within the nation's borders.
Further projections indicate continued growth, albeit at a moderating pace. As of July 1, 2025, the population of Iran is projected at 92,417,681, or 92.42 million. Specifically, on Thursday, July 3, 2025, the population is estimated to be 92,418,311. This growth is driven by a daily average of 3,083 births and 1,228 deaths, resulting in a current annual growth rate of 0.86%. This rate positions Iran at the 111th highest among 237 countries and dependent territories in 2025, indicating a significant shift from its historical rapid expansion.
Historical Growth and Modern Shifts in Iran's Population
A Century of Dramatic Change
The story of Iran's population is one of dramatic transformation, particularly over the latter half of the 20th century. Iran's population increased dramatically during the later half of the 20th century, soaring from relatively modest numbers to reach about 80 million by 2016. This period of explosive growth was fueled by high birth rates and improvements in healthcare, leading to lower mortality rates and increased life expectancy. The increase of the population size by 454.6% in 73 years underscores the profound demographic shift that has occurred within a relatively short historical span.
For context, the total population for Iran in 2022 was 89,524,246, representing a 1.21% increase from 2021. This sustained growth has made Iran one of the most populous nations in the region, with its demographic trends having significant implications for resource allocation, economic development, and social planning. The sheer scale of this growth has shaped everything from urban planning to educational infrastructure, leaving an indelible mark on the nation's fabric.
The Recent Slowdown in Birth Rates
Despite the historical trajectory of rapid expansion, recent years have witnessed a significant shift. In recent years, however, Iran's birth rate has dropped significantly. This decline is a critical factor influencing the country's current and projected population growth. While the "Data Kalimat" does not provide a specific Total Fertility Rate (TFR) number, the mention of a significant drop in birth rates directly implies a declining TFR. This trend is often associated with factors such as increased female education and workforce participation, urbanization, access to family planning, and changing societal norms regarding family size. This represents a dramatic shift from the current demographic structure, moving towards a potentially older population in the future if current trends continue.
Projected Population and Growth Rates: What the Future Holds
Understanding the future trajectory of the population in Iran is crucial for long-term planning. As highlighted, the population is projected at 92.42 million as of 2025, compared to 91.57 million in 2024. This indicates a continued, albeit slower, upward trend. The population growth rate in 2025 is projected at 0.86 percent. While still positive, this rate is considerably lower than the rapid growth observed in previous decades. This deceleration in growth means that while the overall population size will continue to increase for some time, the pace of that increase is slowing down.
These projections are based on detailed demographic models that consider current birth and death rates, as well as migration patterns. Although specific immigration figures are not detailed in the provided data, migration, alongside births and deaths, is a fundamental component of population change. The overall trend suggests that Iran is moving towards a more mature demographic profile, with implications for its workforce, social security systems, and healthcare demands in the coming decades. Interactive data visualizations, as mentioned in the provided data, would be invaluable tools for exploring these complex demographic trends further.
Iran's Demographic Structure: Age and Gender
Sex Ratio and Median Age
The internal structure of Iran's population offers valuable insights into its societal makeup. Iran's population structure shows a slightly higher male to female ratio of 1.03 to 1. This means that for every 100 females, there are approximately 103 males. Specifically, there are 46.95 million males and 45.47 million females in Iran. This slight imbalance is common in many populations, often attributed to higher male birth rates and sometimes differential mortality rates across age groups.
The median age is another critical indicator. The median male age is 34.21 years old, and the median female age is 34.61 years old. The overall median age for the population of Iran (mid-2025) suggests a relatively young to middle-aged population, indicating a substantial working-age cohort. However, as birth rates decline and life expectancy potentially increases, this median age is expected to rise over time, leading to an aging population structure.
The Population Pyramid and Dependency Ratio
A population pyramid graphically illustrates the age and sex structure of a population, providing a visual representation of cohorts by age group. While a specific pyramid is not provided in the "Data Kalimat," the information on median age and sex ratio hints at its shape. Typically, countries that have experienced rapid population growth followed by a decline in birth rates will show a broader base (larger young cohorts) that narrows significantly at older ages, with a noticeable constriction in the younger age groups reflecting the recent drop in births. This shift impacts the dependency ratio, which measures the proportion of dependents (children and elderly) per working-age person. As the median age rises and the birth rate falls, the dependency ratio can shift from being dominated by youth dependency to old-age dependency, posing different challenges for social welfare and economic productivity.
Urbanization: A Defining Trend for Population in Iran
From Rural to Urban: A Rapid Transformation
One of the most profound demographic shifts in Iran has been its rapid urbanization. Iran has one of the highest urban population growth rates in the world. This trend reflects a global movement of people from rural areas to cities in search of better economic opportunities, education, and services. From 1950 to 2002, the urban proportion of the population increased dramatically from 27% to 60%. This represents a monumental societal transformation, changing the face of the country and the daily lives of its citizens.
The pace of urbanization is projected to continue its upward trajectory. The United Nations (UN) predicts that by 2030, 80% of the population will live in urban areas. This projection highlights the ongoing magnetism of cities and the continued rural-to-urban migration that reshapes Iran's demographic map. Such rapid urbanization brings with it both opportunities for economic growth and challenges related to infrastructure, housing, and environmental sustainability.
Major Urban Centers and Internal Migration
The significant increase in urban population is largely due to internal migration. Most internal migrants have settled near the cities of Tehran, Isfahan, Karaj, Ahvaz, and Mashhad. Tehran, being the nation's capital, largest city, and financial center, naturally acts as a major magnet for migrants seeking opportunities. Its immense size and economic vibrancy draw people from across the country, contributing to its ever-expanding metropolitan area.
The concentration of population in these major urban centers has led to significant urban sprawl and increased demand for public services. Understanding these migration patterns is crucial for urban planning and ensuring equitable development across Iran's 31 provinces. The dynamics of these urban hubs play a central role in the overall demographic narrative of the population in Iran.
Population Distribution Across Provinces
Iran is officially an Islamic Republic, divided into five regions with 31 provinces. While Tehran is the nation's capital and largest city, the population of Iranian provinces and counties in 2021 would show a varied distribution across these administrative divisions. Each province has its unique demographic characteristics, influenced by factors such as economic activity, natural resources, and historical settlement patterns. For instance, provinces containing the major urban centers like Tehran, Isfahan, and Mashhad would naturally have higher population densities compared to more rural or less developed regions.
Understanding this provincial distribution is vital for regional development strategies, resource allocation, and political representation. It also highlights the diverse ethnic and cultural groups that constitute the population in Iran, which Fanack provides an overview of, including a description of its ethnicities and other demographics. This includes a longstanding Jewish community, despite the nation's official stance as an Islamic Republic known for its hostility to Israel.
Life Expectancy and Mortality Data
Health data provides crucial context for understanding population dynamics. The World Health Organization (WHO) offers an overview for Iran (Islamic Republic of), containing the latest population, life expectancy, and mortality data. While specific figures for life expectancy are not provided in the "Data Kalimat," the fact that it is tracked alongside mortality data indicates its importance in demographic analysis. Generally, improvements in healthcare, sanitation, and nutrition lead to increased life expectancy and lower mortality rates, contributing to population growth or at least a slower decline in populations with very low birth rates.
The daily figures of 3,083 births and 1,228 deaths highlight the ongoing natural increase in Iran's population. A lower death rate, coupled with a still-positive birth rate, ensures continued growth, even as the overall growth rate moderates. These figures are essential for public health planning, resource allocation for the elderly, and understanding the overall health status of the population in Iran.
The Global Context: Iran's Place in World Population
To fully appreciate the scale of Iran's population, it's helpful to place it within a global context. The population of Iran is equivalent to 1.12% of the world's total population. This makes Iran a significant demographic player on the global stage, especially given its strategic geographical location and geopolitical importance. While 1.12% might seem like a small fraction, it represents tens of millions of people, making Iran one of the more populous countries globally.
This global share underscores the relevance of Iran's demographic trends not just for the country itself, but for regional and international dynamics. Changes in the population in Iran, whether in terms of size, age structure, or urbanization, have ripple effects that extend beyond its borders, influencing everything from labor markets to environmental concerns on a broader scale. Monitoring these trends with interactive data visualizations, as suggested, provides a deeper understanding of Iran's evolving role in the world.
Conclusion
The journey through Iran's population dynamics reveals a country in the midst of significant demographic transformation. From a period of explosive growth in the late 20th century to a more moderated pace today, characterized by a notable drop in birth rates, Iran's demographic profile is continuously evolving. With a current population of over 91 million and projections pointing towards 92.42 million by 2025, the sheer scale of the population in Iran remains substantial, placing it as a significant global demographic entity.
Key takeaways include the ongoing urbanization trend, with the vast majority of Iranians expected to reside in cities by 2030, and the subtle shifts in age and gender distribution. These changes have profound implications for Iran's future, impacting its economy, social services, and environmental landscape. Understanding these complex trends is not merely an academic exercise; it's crucial for informed policy-making and sustainable development. We encourage you to explore more about these fascinating demographic shifts. What are your thoughts on Iran's population trends? Share your insights in the comments below, or explore other related articles on our site to deepen your understanding of global demographics.

World population could peak at 8.5 billion people by the 2050s, study
Population Year 2022 - Worldmapper
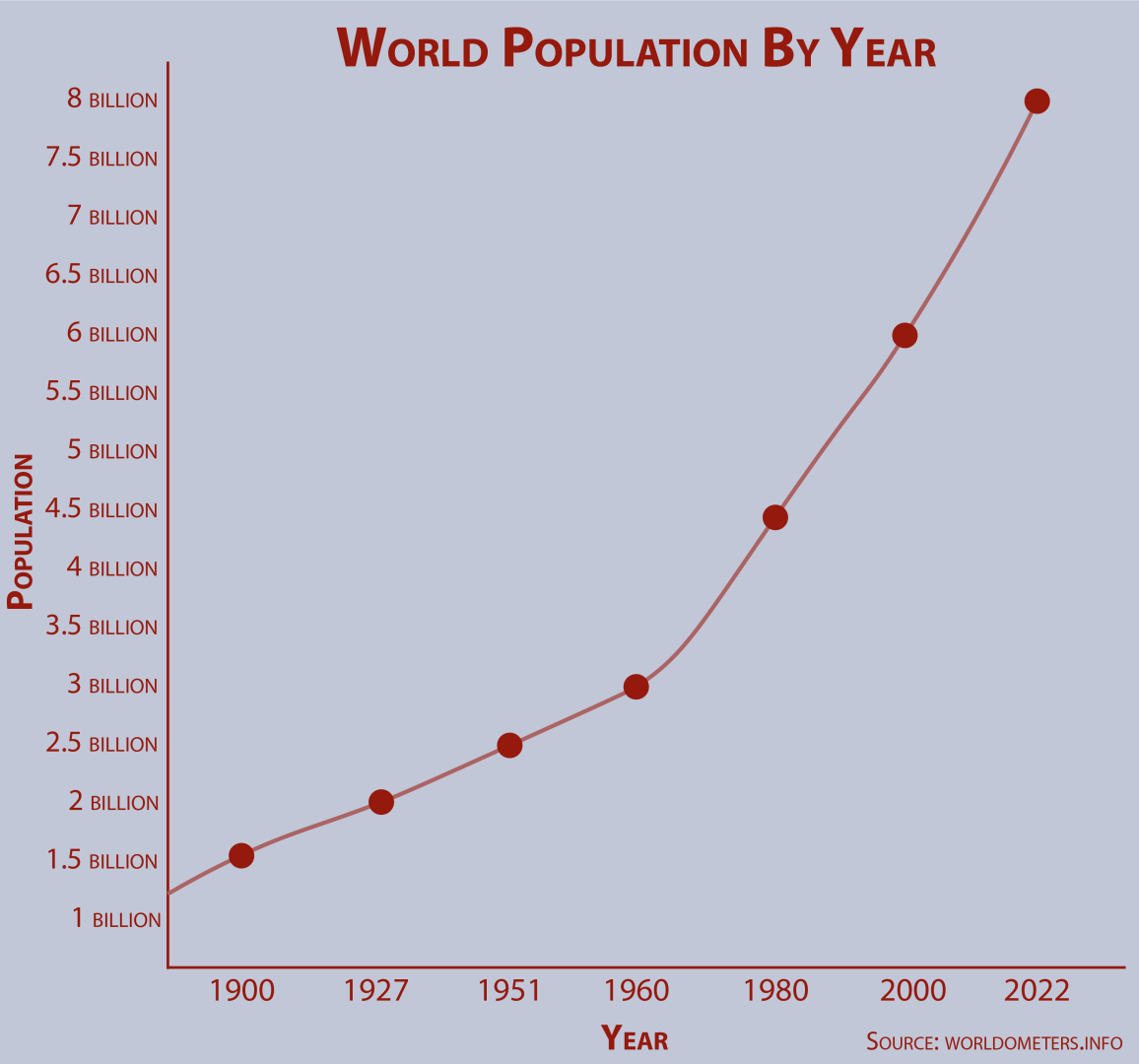
Global population reaches eight billion – The Reflector